Grafen Oksit Nanoparçacıkları İçeren Nanoakışkan
Grafen Oksit Nanoparçacıkları İçeren Nanoakışkanın Taşınım Isı Transferi ve Basınç Düşüşü Artışı Üzerindeki Etkisinin Düz Bir Boruda Deneysel Olarak Araştırılması
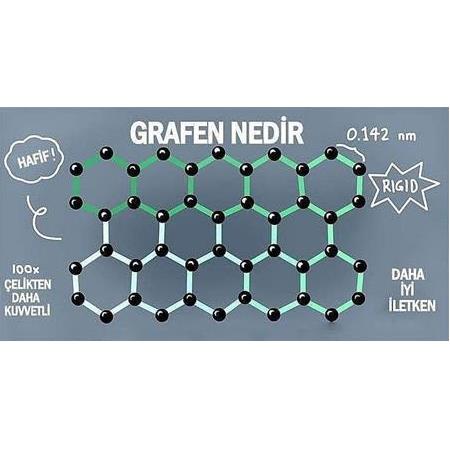
Bu çalışmada, grafen oksit (GO)-su nanoakışkanının taşınım ısı transferi üniform duvar ısı akılı dairesel bir bakır boru boyunca laminer akış için deneysel ve sayısal olarak incelenmiştir. Deneysel çalışmada, grafen oksit-su nano-akışkanının ısı transferi artışı ve basınç düşüşü özellikleri değerlendirilirken, sayısal çalışmada korunum denklem-leri üç boyutlu olarak sonlu hacim yöntemi olan CFD paket programının (ANSYS 15.0-FLUENT) kullanılmasıyla tek fazlı akışkan kabulüyle çözülmüştür. Taban akışkanı olarak kullanılan saf suyun ısı transfer katsayısı ve basınç düşüşü ölçülmüş ve ilgili bağıntıdan elde edilen sonuçlarla karşılaştırılmıştır. Sayısal çalışmada elde edilen boru yüzey sıcaklık değerleri nanoakışkan için deneysel sonuçlarla karşılaştırıldığında ortalama %2 hata ile birbiriyle uyumlu olduğu görülmüştür. Çalışmada, %0,01 ve %0,02 hacimsel konsantrasyonlu GO-su nanoakışkanının ısı transferi artışında ısı akısının, nanoparçacık hacimsel konsantrasyonunun ve hacimsel debinin etkileri sunulmuş-tur. %0,02’lik konsantrasyonda GO-su nanoakışkanının ısı taşınım katsayısı artışı değeri (hnf /hbf), 1,5 l/dk’lık debi (Re=2023) ve 2536.62 W/m 2 (350 W) ısı akısı değerinde %13,9 olmaktadır. Bununla birlikte, yük kaybı (h K) ve sürtünme faktörü için en yüksek artışlar %0,02 GO ve 1,5 l/dk’lık debide sırasıyla %8,37 ve %7,95’tir. Sonuçlar, GO nanoakışkanının ısı transferi uygulamalarında geleneksel çalışma akışkanlarına iyi bir alternatif olarak kulla-nılabileceğini göstermektedir Anahtar Kelimeler: Nanoakışkan, grafen oksit (GO), taşınım ısı transfer katsayısı ABSTRACT In this paper, convective heat transfer of graphene oxide-water (Graphene oxide) nanofluid in a laminar flow through a circular copper pipe with uniform wall heat flux is investigated experimentally and numerically. In experimental investigation, it is evaluated the heat transfer characteristics and the pressure drop of the graphene oxide (GO)-water nanofluid when in numerical study, the finite volume method (ANSYS 15.0-FLUENT) is employed to solve the conservation equations (continuity, momentum and energy equations) in three dimensional domains by assuming single phase flow. The heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop of the DI (distilled)-water used as base fluid is measured and compared with the corresponding data from the correlation. The datas of nanofluid for surface temperature of the tube is satisfied within a 2% error for the numerical work compared with experimental results. The effects of the heat flux, volumetric concentration and flow rate on the enhancement of the heat transfer of GO-water nanofluid with volumetric concentrations of 0,01% and 0,02% are presented in the study. The value of convective heat transfer coefficient enhancement (hnf /hbf) of the GO with 0,02% volumetric concentration and flow rate of 1,5 l/min (Re=2023) is 13,9% for the heat flux value of 2536.62 W/m 2 (350 W). However, the max. increases in head loss and friction factor with 0,02% GO and 1,5 l/min are 8,37% and 7,95% respectively. Finally, the results reveals that the GO-water nanofluid can be used as a good alternative conventional working fluids in heat transfer applications.
Yorum yapabilmek için giriş yapmalısınız.


Yazar hakkında